In addition to protocols, it's crucial to understand the role of addressing in data communication. Addressing involves assigning unique identifiers to devices and systems within a network, facilitating accurate data transmission. Each device on a network has a distinct address that helps in routing information to the correct destination.
Furthermore, data communication often involves the concept of encapsulation, where data is wrapped in a specific format before transmission. This encapsulation process helps in organizing and structuring data, ensuring that it can be correctly interpreted by the receiving device.
Another important aspect is the distinction between analog and digital signals in data communication. Analog signals represent continuous waves, while digital signals are discrete and take on specific values. The conversion between these signal types is crucial in modern communication systems, as digital signals are more resilient to noise and distortion.
Security is a paramount concern in data communication. Encryption plays a pivotal role in safeguarding sensitive information during transmission. It involves encoding data in a way that only authorized parties can decipher, adding a layer of protection against unauthorized access or interception.
Additionally, Quality of Service (QoS) mechanisms are implemented to prioritize and manage the flow of data in a network. QoS ensures that critical applications receive sufficient bandwidth and resources, optimizing the overall performance of the communication system.
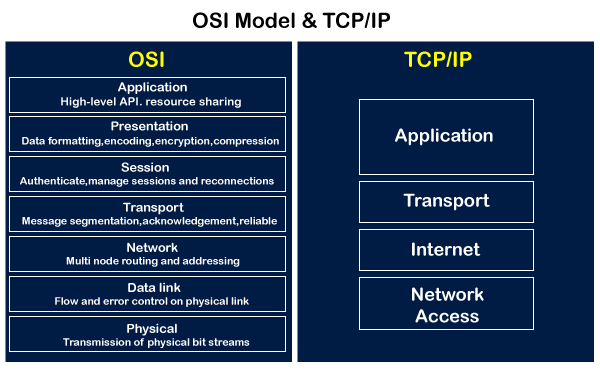
In the context of network models, it's worth noting that the OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) model consists of seven layers, each responsible for specific aspects of communication. These layers include the physical, data link, network, transport, session, presentation, and application layers. Similarly, the TCP/IP model, which is widely used in internet communication, comprises the link, internet, transport, and application layers.
Understanding these additional elements enhances the comprehension of data communication, providing a comprehensive view of the various factors at play in efficient and secure information exchange across networks.
This article will help you:
- Grasp the importance of network reference models
- Recognize the advantages of layered architecture in network models.
- Enumerate the seven layers of the OSI reference model
- Understand the operations of OSI layers and the services they provide.
- Compile a list of functions and responsibilities of each OSI model layer
- Understand the operations of TCP/IP layers and their respective services.
- Compile a list of functions and responsibilities of each TCP/IP model layer
- Summarize the roles of OSI layers and compare them with the functions of TCP/IP layers.